What is a stent?
Discover our latest podcast
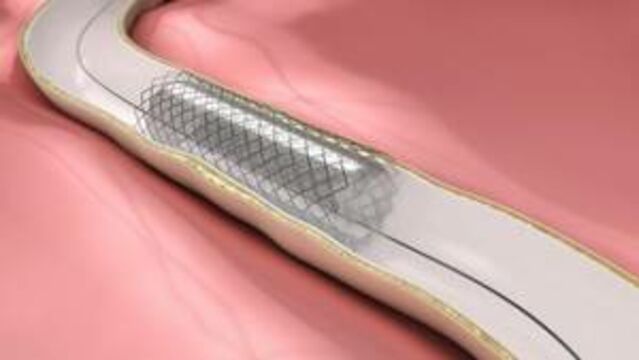
A stent is a metal prosthesis in the shape of a tube placed in the coronary arteries to prevent them from becoming blocked. Usually it is put in through an angioplasty.
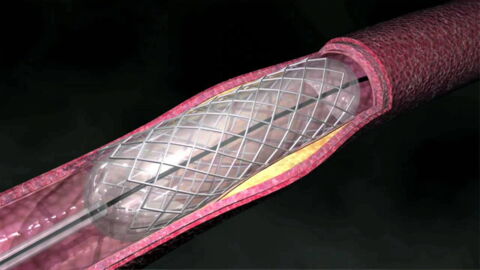
The angioplasty is a surgical method which aims to dilate the arteries. It is carried out when there is fatty waste, called atheroma plaque, accumulates inside the coronary arteries, reducing the flow of blood towards the heart. The angioplasty consists of carrying out a small incision in the thigh, in order to access the femoral artery. A guiding thread is then inserted and pushed through just to the site of obstruction. A catheter fixed to a deflated balloon is transported along the guiding thread. When it it inflated, the balloon squeezes the plaque against the arterial wall and widens the artery. The blood can therefore circulate normally.
The stent is placed around the catheter. After the balloon has inflated, the stent spreads out and sticks to the wall. It then remains in place, preventing another blockage in the coronary artery.
Types of stents
There are two different types of stents: naked stents and active stents. Naked stents are solely composed of stainless steel and can be rejected by the body.
Active stents are covered in an antiproliferative substance which can reduce the risk of a new stenosis (narrowing of a blood vessel) in the atheroma plaque. It is made up of polyactic avid which is entirely absorbed by the artery wall, and limits the appearance of clots (thrombosis). However, there is more risk of a myocardiac attack than with a naked stent. The active stent has been used more commonly in recent years.
Disadvantages of a stent
Placing a stent in the body presents several disadvantages. It does require follow up treatment in the form of anti-platelet medication, made up of aspirin and clopidogrel) over several months. This is necessary in order to avoid a thrombosis (blood clot) in the artery. Implanting the stent can also provoke internal bleeding in the case of a surgical operation or traumatic shock. Therefore, a restenosis can occur six months after the operation (approximately 7% of active stent cases, and between 10 to 30% in naked stent cases).