Definition: what is an angioplasty?
Discover our latest podcast
An angioplasty is a surgical procedure performed to dilate a coronary artery. It aims to re-establish the flow of blood following a blockage in an artery. It is used when a blood vessel narrows or during coronary stenosis.
Over time, fat deposits can accumulate on the walls of the arteries. These plaques, known as atheroma, are formed by cholesterol, fibre tissue and inflammatory cells. Little by little, they block the vascular lumen and slow down the blood flow.
If a coronary artery is affected by this, it can cause problems for blood circulation towards the heart, thus meaning there is no longer a sufficient supply of blood. This can cause angina pectoris, or if the vessel is blocked completely, myocardial infarction.
The angioplasty procedure
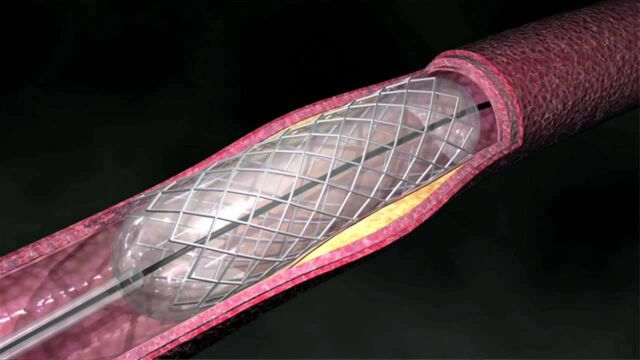
An angioplasty involves inserting a deflated balloon attached to a catheter into the vessel where the blockage is. In order to do this, a small incision is made in the thigh under local anaesthetic and the catheter is then inserted into the femoral artery. Once at the point of the blockage, the balloon is inflated using a syringe equipped with a manometer to reduce the atheromatous plaque by compressing it into the wall. This then increases the diameter of the coronary artery. The balloon is then deflated so that blood can start flowing through the artery again.
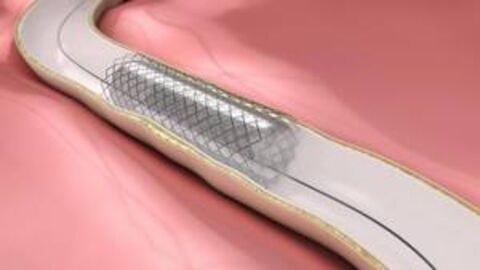
In order to avoid plaque forming again, a stent is often placed around the catheter. This is a metal prosthesis in the shape of a tube. Once the balloon is inflated, the stent expands and sticks to the wall of the artery. Even when the catheter is removed, the stent remains in place and maintains its shape to keep the artery open.
An angioplasty normally lasts between 45 and 90 minutes. The procedure isn’t painful and doesn’t take long to recover afterwards, with people normally kept in hospital for between 2 to 3 days. However, when a stent is inserted, an antiplatelet treatment based in aspirin and clopidrogel should be taken for a few months afterwards.